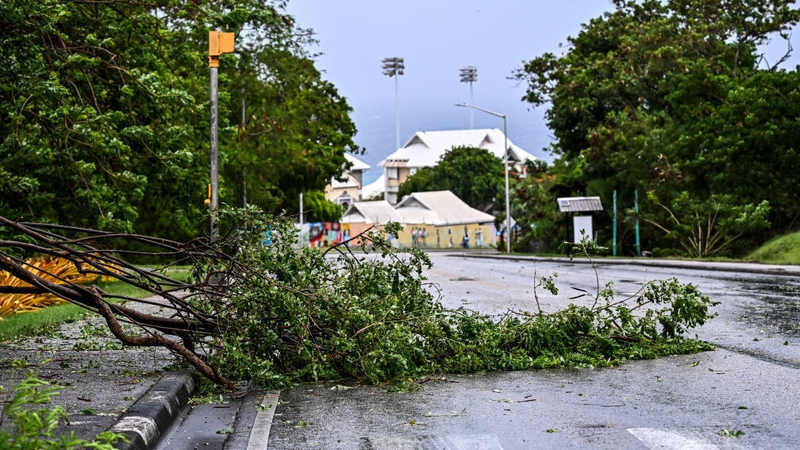
Hurricane Beryl has brought devastating winds and heavy rain to several Caribbean islands as the earliest-ever Category 4 storm churned westward.
Carriacou Island, which is part of Grenada, took a direct hit this morning from the storm's "extremely dangerous eyewall," with sustained winds at upwards of 150 miles (240 kilometers) per hour, the US National Hurricane Center (NHC) said.
Nearby islands, including Grenada and St. Vincent and the Grenadines, also experienced "catastrophic winds and life-threatening storm surge" according to the NHC.
Video obtained by AFP from St. George's in Grenada showed heavy downpours with trees buffeted by gusts.
Posting a video showing large waves, the Office of the Prime Minister of Grenada wrote on Facebook that the tri-island state was "experiencing intense winds and damage".
"This is an extremely dangerous and life-threatening situation," the NHC said. "Residents should not leave their shelter and remain in place through the passage of these life-threatening conditions."
Experts say that such a powerful storm forming this early in the Atlantic hurricane season - which runs from early June to late November - is extremely rare.
It is the first hurricane since NHC records began to reach the Category 4 level in June.
"Only five major (Category 3+) hurricanes have been recorded in the Atlantic before the first week of July," hurricane expert Michael Lowry posted on social media platform X.
Barbados appeared to be spared from the worst of the storm but was still hit with high winds and pelting rain, as officials reported no injuries so far.
The island's meteorological agency downgraded a hurricane warning this afternoon to a wind advisory until 6pm local time (11pm Irish time).
We need your consent to load this comcast-player contentWe use comcast-player to manage extra content that can set cookies on your device and collect data about your activity. Please review their details and accept them to load the content.Manage Preferences
Barbados seems to have "dodged a bullet," Minister of Home Affairs and Information Wilfred Abrahams said in an online video, but nonetheless "gusts are still coming, the storm-force winds are still coming" he said.
The hurricane warning was also lifted in Tobago, the smaller of the two islands that make up Trinidad and Tobago, officials said.
The storm prompted the cancellation of schools on Monday in several of the islands, while a meeting this week in Grenada of the Caribbean regional bloc CARICOM was postponed.
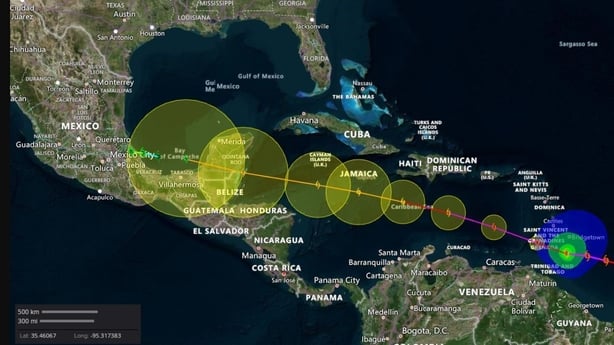
Beryl is expected to remain a "powerful hurricane" as it continues churning westward, the NHC said, with tropical storm warnings or watches announced in Jamaica and in parts of the Dominican Republic and Haiti.
The NHC also warned the Cayman Islands and areas on the Yucatan Peninsula to monitor the storm's progress.

Beryl became the first hurricane of the 2024 Atlantic season early Saturday morning and quickly strengthened to Category 4, the first ever to reach that level in June, according to NHC records.
A Category 3 or higher on the Saffir-Simpson scale is considered a major hurricane, and a Category 4 storm packs sustained winds of at least 130 miles per hour (209 kilometers per hour).
As Beryl struck Carriacou, it was packing maximum sustained winds that had increased to 241kph, the NHC said.
We need your consent to load this rte-player contentWe use rte-player to manage extra content that can set cookies on your device and collect data about your activity. Please review their details and accept them to load the content.Manage Preferences
Beryl is expected to remain powerful as it moves across the Caribbean, the NHC said, warning residents and officials in the Lesser Antilles, Hispaniola, Jamaica, the Cayman Islands and the remainder of the northwestern Caribbean to carefully monitor its progress.
The US National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration said in late May that it expects this year to be an "extraordinary" hurricane season, with up to seven storms of Category 3 or higher.
The agency cited warm Atlantic Ocean temperatures and conditions related to the weather phenomenon La Nina in the Pacific for the expected increase in storms.
Extreme weather events including hurricanes have become more frequent and more devastating in recent years as a result of climate change.

